10 COVID-19 vaccine facts Here are 10 key facts about COVID-19 vaccines. 1. COVID-19 vaccines are safe and effective They have undergone rigorous testing and have been proven to protect against severe illness, hospitalisation, and death caused by COVID-19. 2. Vaccines reduce transmission Whilst COVID-19 vaccines are not specifically authorised to prevent virus transmission, studies […]
Read MoreNormal haemoglobin (Hb) levels by age and gender In this article, we will describe normal haemoglobin (Hb) levels, by age and gender. Normal haemoglobin levels depend on the age and, beginning in adolescence, the gender of the person. Newborn 170 – 220 g/L One (1) week 150 – 200 One (1) month 110 – 150 […]
Read MoreWhy do humans like music so much? # In this article, we will discuss why do humans like music so much. We don’t know. Babies are not born with an inherent response to (and understanding of) music. And there is no agreed theory of why we like it (and most humans do), and how this […]
Read MoreWhat common pregnancy symptoms do women experience? In this article, we will describe what common pregnancy symptoms women experience. First of all .. pregnancy is a normal. It is not a disease. But there are ‘symptoms’ (i.e. physical changes to your body) that are features of normal pregnancy. Common early pregnancy symptoms include a missed […]
Read MoreWhat are the warning signs of sepsis – and what to do? In this article, we will describe what are the warning signs of sepsis – and what to do. Sepsis is a medical emergency, and should be acted on, as such. Meningococcal rash What is sepsis? Sepsis is a very serious condition in which […]
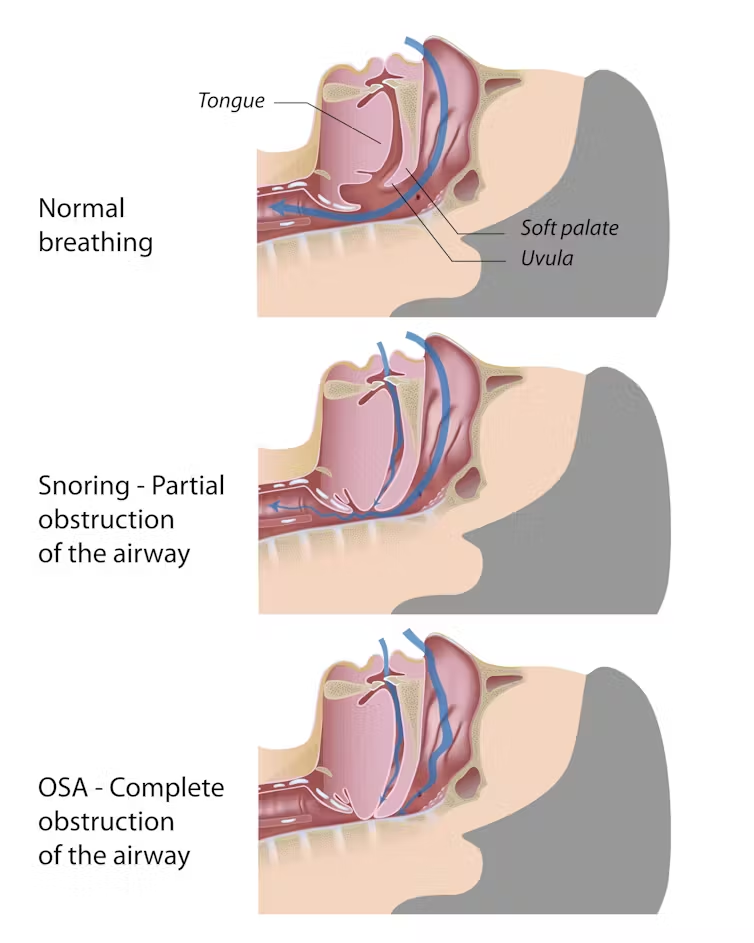
Read MoreWhy do people snore? Snoring occurs when tissues in the upper airway (like the soft palate and uvula) vibrate as air rushes past them during sleep, often due to relaxed throat muscles and a narrowed airway. Here’s a more detailed explanation. Relaxed throat muscles During sleep, the muscles in your throat and mouth relax, which […]
Read MoreWhat is the effect of alcohol on the brain? Alcohol’s impact on the brain is complex and multifaceted. Here’s a breakdown: Short-term effects Impaired cognitive function: Alcohol affects attention, memory, and decision-making skills Mood changes: Alcohol can induce feelings of euphoria, relaxation, or aggression Cerebellar mediated damage: Coordination and balance: Alcohol damages the cerebellum, impairing […]
Read MoreWhat is the duration of AKI? 10-14 days. Renal recovery. Most patients recover (if they survive), and the kidney function usually returns to the baseline level. This usually happens in 10-14 days, and for most people by three weeks. A small number take upto 3 months If the patient is on dialysis at 3 months, […]
Read MoreNHS Interview: 10 common questions and answers In this article, we will describe frequently asked questions in an NHS interview – and suggest answers that will impress your prospective employer. The most important thing is to say something. It’s OK to have opinions and get these across. The panel will know alot about you from […]
Read MoreWhat is an ultrasound – and how is it done? In this article, we will describe what is an ultrasound, and how it is done. An ultrasound scan is a non-invasive medical imaging procedure that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of internal structures within the body. It is done by an x-ray doctor […]
Read More