This is how the AI article summary could look. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
What tests are done for heart disease?
To identify common heart conditions you’ll need to have some tests. These could include:
- Checking your pulse
- Blood pressure
- ECG
- ECHO
- X-rays
- Blood tests.
Examination
Pulse
-
Purpose: Assess heart rate, rhythm, and strength
-
Method: Palpation of peripheral pulses (e.g. radial, carotid)
-
Normal range: 60-100 beats per minute (bpm) at rest
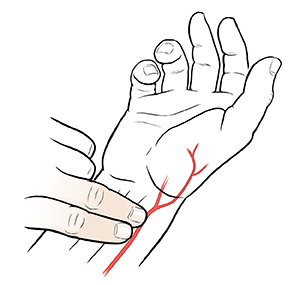
Taking a radial pulse
Blood Pressure
-
Definition: Pressure within blood vessels as the heart contracts and relaxes
-
Measurement: Recorded as systolic (higher) and diastolic (lower) pressures
-
Normal range: Approximately 100/70 to 135/85 mmHg
-
Variability: Fluctuates throughout the day; can be affected by activity, stress, and the ‘white coat effect’
-
Monitoring: May involve 24-hour ambulatory monitoring (at home).
Electrical Tests
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
-
Purpose: Record electrical activity of the heart
-
Method: Non-invasive, painless test with electrodes placed on the chest
-
Duration: Approximately 5-10 minutes.
24-hour Ambulatory ECG
-
Purpose: Monitors cardiac activity over 24 hours
-
Method: Wearable device with electrodes attached to a belt
-
Use: Records abnormalities and symptoms during daily activities.
Stress Test (Exercise Tolerance Test, ETT)
-
Purpose: Assess cardiac function during exercise
-
Method: ECG recording while walking on a treadmill
-
Use: Evaluates heart response to physical stress.
Imaging Tests
Echocardiogram
-
Purpose: Ultrasound scan of the heart
-
Method: Transducer placed on the chest with gel
-
Use: Assesses heart size, muscle contraction, valve function, and blood flow.
Chest x-ray
-
Purpose: Evaluate heart size and detect chest disorders
-
Method: Standard radiographic imaging
-
Use: Provides information on heart size, shape, and lung abnormalities.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
-
Purpose: Detailed imaging of heart structure and blood vessels
-
Method: Painless scan using a magnetic field
-
Use: Useful for assessing cardiac anatomy and blood supply.
Cardiac Computed Tomography (Cardiac CT)
-
Purpose: Detailed 3D imaging of the heart
-
Method: Specialised x-ray machine
-
Use: Evaluates coronary arteries and cardiac structure (alternative to coronary angiogram).
Thallium Scan (Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy)
-
Purpose: Assess blood flow to the heart muscle
-
Method: Injection of radioactive substance (thallium) and imaging with a special camera
-
Use: Alternative to stress test; evaluates coronary artery disease.
Coronary Angiogram
-
Purpose: Examine coronary arteries for disease
-
Method: Insertion of catheter into a blood vessel, injection of contrast dye, and x-ray imaging
-
Use: Diagnoses coronary artery disease, assesses narrowing or blockages.
Blood Tests
-
Purpose: Rule out underlying causes of cardiac symptoms,
monitor medication
-
Common tests:
-
Full Blood Count (FBC)
-
Urea and Electrolytes (U&Es)
-
Glucose
-
Liver and thyroid function tests
-
Troponin (for suspected myocardial infarction)
-
Cholesterol and lipid profile
-
Natriuretic peptides (e.g. BNP) for heart failure.
Other Tests
Tilt Test
