What tests are done for heart disease?
To identify common heart conditions you’ll need to have some tests. These could include:
- Checking your pulse
- Blood pressure
- ECG
- ECHO
- X-rays
- Blood tests.
Examination
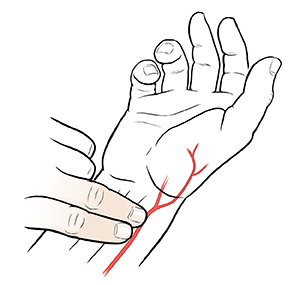
Pulse
-
Purpose: Assess heart rate, rhythm, and strength
-
Method: Palpation of peripheral pulses (e.g. radial, carotid)
-
Normal range: 60-100 beats per minute (bpm) at rest
Taking a radial pulse
Blood Pressure
-
Definition: Pressure within blood vessels as the heart contracts and relaxes
-
Measurement: Recorded as systolic (higher) and diastolic (lower) pressures
-
Normal range: Approximately 100/70 to 135/85 mmHg
-
Variability: Fluctuates throughout the day; can be affected by activity, stress, and the ‘white coat effect’
-
Monitoring: May involve 24-hour ambulatory monitoring (at home).
Electrical Tests
Electrocardiogram (ECG)
-
Purpose: Record electrical activity of the heart
-
Method: Non-invasive, painless test with electrodes placed on the chest
-
Duration: Approximately 5-10 minutes.
24-hour Ambulatory ECG
-
Purpose: Monitors cardiac activity over 24 hours
-
Method: Wearable device with electrodes attached to a belt
-
Use: Records abnormalities and symptoms during daily activities.
Stress Test (Exercise Tolerance Test, ETT)
-
Purpose: Assess cardiac function during exercise
-
Method: ECG recording while walking on a treadmill
-
Use: Evaluates heart response to physical stress.
Imaging Tests
Echocardiogram
-
Purpose: Ultrasound scan of the heart
-
Method: Transducer placed on the chest with gel
-
Use: Assesses heart size, muscle contraction, valve function, and blood flow.
Chest x-ray
-
Purpose: Evaluate heart size and detect chest disorders
-
Method: Standard radiographic imaging
-
Use: Provides information on heart size, shape, and lung abnormalities.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
-
Purpose: Detailed imaging of heart structure and blood vessels
-
Method: Painless scan using a magnetic field
-
Use: Useful for assessing cardiac anatomy and blood supply.
Cardiac Computed Tomography (Cardiac CT)
-
Purpose: Detailed 3D imaging of the heart
-
Method: Specialised x-ray machine
-
Use: Evaluates coronary arteries and cardiac structure (alternative to coronary angiogram).
Thallium Scan (Myocardial Perfusion Scintigraphy)
-
Purpose: Assess blood flow to the heart muscle
-
Method: Injection of radioactive substance (thallium) and imaging with a special camera
-
Use: Alternative to stress test; evaluates coronary artery disease.
Coronary Angiogram
-
Purpose: Examine coronary arteries for disease
-
Method: Insertion of catheter into a blood vessel, injection of contrast dye, and x-ray imaging
-
Use: Diagnoses coronary artery disease, assesses narrowing or blockages.
Blood Tests
-
Purpose: Rule out underlying causes of cardiac symptoms, monitor medication
-
Common tests:
-
Full Blood Count (FBC)
-
Urea and Electrolytes (U&Es)
-
Glucose
-
Liver and thyroid function tests
-
Troponin (for suspected myocardial infarction)
-
Cholesterol and lipid profile
-
Natriuretic peptides (e.g. BNP) for heart failure.
-
Other Tests
Tilt Test
-
Purpose: Assess symptoms of light-headedness or dizziness
-
Method: Monitor blood pressure and heart rate while lying down and standing up
-
Use: Evaluates orthostatic intolerance (blood pressure falls too much on standing) and autonomic function.