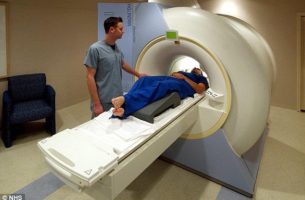
What is an MRI – and how is it done? In this article, we will describe what is an MRI, and how it is done. An MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scan is a painless and non-invasive medical imaging procedure that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the internal structures […]
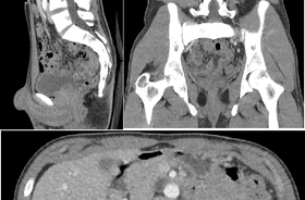
Read MoreWhat is a CT scan – and how is it done? In this article, we will describe what is a CT scan, and how it is done. A CT (Computed Tomography) scan is a painless medical imaging test that uses x-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the body. Here’s a step-by-step […]
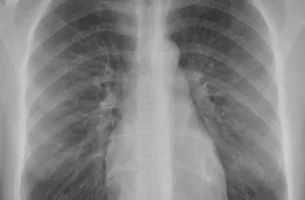
Read MoreWhat is a chest xray – and how is it done? A normal chest x-ray (CXR) In this article we will describe what is a chest xray – and how it is done. A chest x-ray is a painless non-invasive medical imaging test used to take pictures of the lungs, heart, and surrounding tissues. […]
Read MoreBasic principles of x-ray analysis A normal chest x-ray The interpretation of an x-ray film requires sound anatomical knowledge, and an understanding that different tissue types absorb x-rays to varying degrees: High density tissue (e.g. bone) – absorb x-rays to a greater degree, and appear white on the film. Low density tissue (e.g. lungs) – absorb […]
Read MoreChest x-ray interpretation: 7 steps This is a normal chest x-ray. In this article, we will describe how to interpret a chest x-ray in 7 steps (ABCDEFG), after correctly identifying the patient, and describing the type of x-ray. You need to know your anatomy. Firstly .. identification, and what type of chest x-ray is it? […]
Read MoreMost common causes of a high amylase Acute pancreatitis Pancreatic or bile duct blockage Cholecystitis and viral hepatitis Cancer of the pancreas, ovaries, or lungs Perforated ulcer or intestinal obstruction Infection of the salivary glands (such as mumps) or a blockage of the salivary gland duct Macroamylasaemia Tubal pregnancy (may have burst open). A normal blood amylase […]
Read MoreA normal amylase level A normal amylase level is 30-120 u/L. What is amylase? The pancreatic enzyme, amylase is normally secreted into the gastro-intestinal tract (duodenum). Diseases of the pancreas (e.g. pancreatitis or pancreatic cancer) or salivary gland(s), cause amylase to enter the bloodstream. Circulating levels may rise to 30 times the normal values, and […]
Read MoreMost common causes of a high CRP C-Reactive Protein (CRP) is a protein produced by the liver in response to inflammation in the body. A raised CRP level indicates inflammation, which can be caused by various conditions. Here are some common causes of a raised CRP. Infection Bacterial infection: e.g. Pneumonia, urinary tract infection (UTI), […]
Read MoreWhat is CRP (C-reactive protein)? C-reactive protein (CRP) is a protein produced by the liver that increases in response to inflammation in the body, serving as a marker for inflammation, infection and other disease processes. CRP is an acute-phase reactant protein, meaning its levels rise rapidly in response to inflammation. How it works When the […]
Read MoreHow to jump the NHS waiting list by 6 months This is alot easier than you might think, but all the top tips below require some work from you. If you do them all, you can jump the waiting list by 6 months – even more if needed. We will now give you 10 ways […]
Read More