Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a long-term condition where the kidneys do not work as well as they should, or are damaged in some way. It is not always serious.
It affects 10% of the population, but only 1% of them will need dialysis or a kidney transplant – i.e. 1 in 1000 of the population.
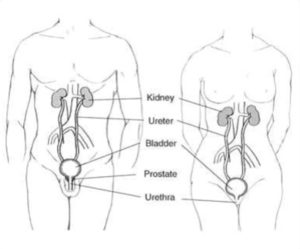 Urinary tract
Urinary tract
The kidneys are part of the urinary tract. This is a group of organs that act as the body’s dustmen, and get rid of waste products from food and extra water in the blood for you, 24 hours a day.
The disease is called ‘chronic’ because the damage to your kidneys happens slowly over a long period of time – usually over months or years.
This damage can cause wastes to build up in your blood and body; or some other evidence damage to the kidneys (e.g, protein in urine).
CKD can also cause other health problems, especially related to the heart and blood pressure. In most people it is a ‘silent disease’, i.e. they do not know they have it – like high blood pressure, high cholesterol and early diabetes.
Let’s start with a definition.
Simple definition 1 (simple): a long-term condition where the kidneys do not work as well as they should, or are damaged in some way.
Precise definition 2 (more complex and accurate, used by doctors): with 2 types ..
This definition is based on the 2024 KDIGO CKD guideline (Stevens, 2024).
Note. In other words, in some cases of CKD there is evidence of kidney damage but normal renal function (normal GFR and creatinine).
 5 Stages of CKD
5 Stages of CKD
The diagnosis of CKD is largely based on a classification of its severity, based on GFR (glomerular filtration rate) – the higher the eGFR, the better.
Normal GFR in humans is 90-120 mls/min.
The GFR is calculated from the blood creatinine level (normal range 60-120 mcmol/L) – i.e. the lower the creatinine, the higher is the GFR, the better.
But what do these stages really mean?
As we have said, about 1 in 10 people have CKD, i.e. its very common. Fortunately in most people, it is mild and more of a risk factor than disease.
However, in 1 in 100 people with CKD, kidney function gets worse over time, and develop kidney failure (stage 5 CKD).
This equates to 1 in 1000 of the population. They will then need dialysis or a kidney transplant.
Age is the primary risk factor for CKD:
Approximately 70,000 people in the UK are on dialysis or have a transplant. This means that each GP will have two such patients ‘on their books’. This is why they cannot be expected to be experts in the condition.
We have described what is chronic kidney disease (CKD). Chronic kidney disease is an important focus of this website. So, hopefully by reading our articles you will get a better understanding of what is chronic kidney disease.