This is how the AI article summary could look. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
Basic liver anatomy
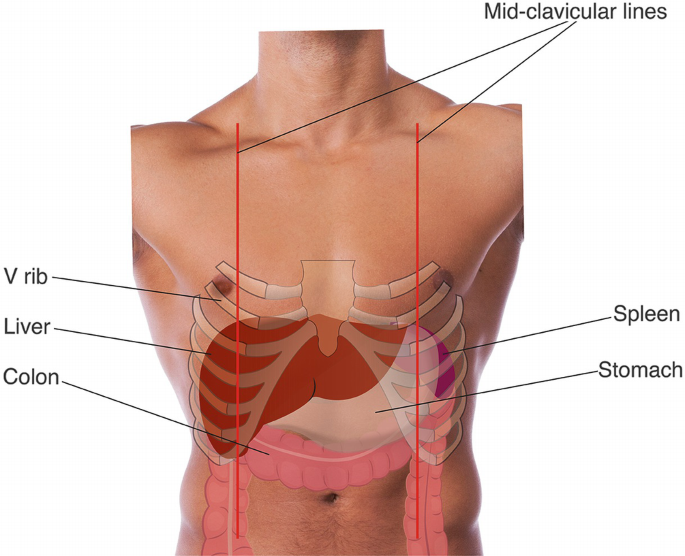
The liver is a vital organ located in the upper right side of the abdominal cavity. It is the largest solid organ in the body.
It is a giant filter and factory and larder for the body. It has 500 functions, far more than all other organs.
 Liver lobule
Liver lobule
Overview of liver basic anatomy
- Structure:
- The liver is a large, wedge-shaped organ with two main lobes (right and left), plus two smaller lobes (caudate and quadrate).
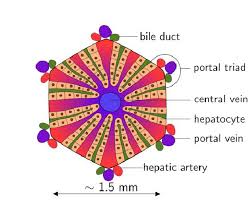
- Lobes are divided into functional units called lobules (1000 of them) – which contain hepatocytes (liver cells), bile ducts, and branches of the hepatic artery (carrying oxygenated blood), hepatic portal vein (carrying nutrient-rich blood) and hepatic vein – which are the functional units where blood is processed and bile is produced.
- Hepatocytes: These are the basic functional cells of the liver, also known as liver cells.
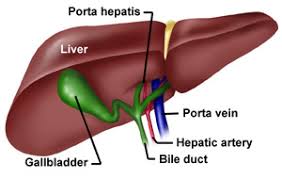
- Bile Ducts: These tubes transport bile (a substance that helps break down fats) from the liver to the gallbladder and the small intestine.
- Covering: It’s covered by a fibrous membrane called Glisson’s capsule.
- Function: The liver plays a crucial role in detoxification (filtering), metabolism (making things), and production of bile and proteins.
- Major Blood Vessels
- The liver is unsual in that it receives blood from two main sources:
- Hepatic Artery: Supplies oxygenated blood to the liver
- Portal Vein: Carries nutrient-rich blood from the digestive system, spleen, and pancreas to the liver
- Hepatic Vein: Drains processed blood from the liver into the inferior vena cava, the main vein that carries blood back to the heart.
- Biliary System: Bile produced by hepatocytes flows into bile ducts, and eventually into the gallbladder for storage.
- Ligaments such as the falciform, coronary, and triangular ligaments attach the liver to the diaphragm and abdominal cavity.
- Porta Hepatis: This is the entry and exit point for the liver’s main blood vessels and common bile duct.
Weight of Liver
The liver’s weight varies by gender but averages about 1.5 kg with men typically having a heavier liver (around 1.8 kg) than women (around 1.3 kg).


 Liver lobule
Liver lobule