This is how the AI article summary could look. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
Basic heart anatomy
The heart is a muscular organ that pumps blood throughout the body.
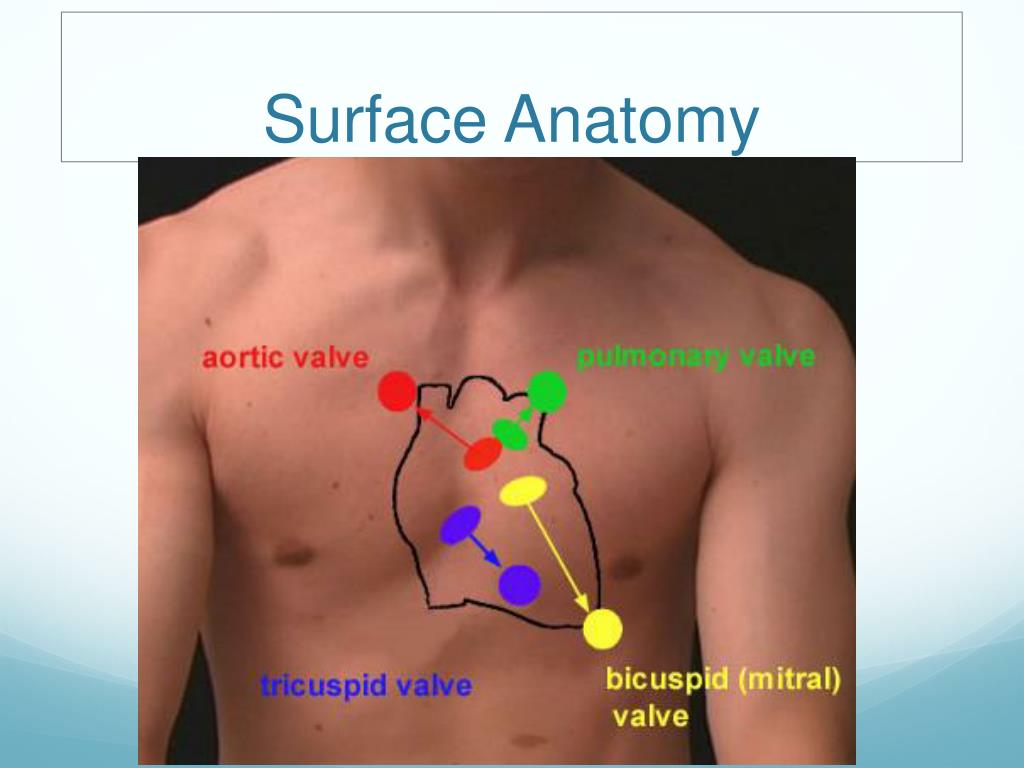
The basic anatomy of the heart includes four chambers: the right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle, which are separated by a muscular wall called the septum.
The heart also has four valves (tricuspid, pulmonary, mitral, and aortic) to ensure one-way blood flow.
It is connected to the body and lungs by major blood vessels such as the vena cava, pulmonary arteries, pulmonary veins, and the aorta.
Overview of basic heart anatomy
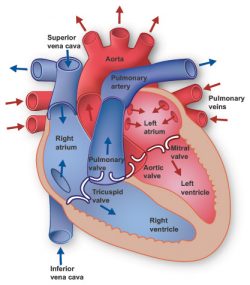
- Chambers: The heart is divided into two sides, each with an upper and a lower chamber (making four chambers in total)
- Right Atrium: The right upper chamber that receives deoxygenated blood from the body.
- Right Ventricle: The right lower chamber that pumps the deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
- Left Atrium: The left upper chamber that receives oxygenated blood from the lungs.
- Left Ventricle: The left lower chamber that pumps the oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
- Blood Flow
- Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium and flows into the right ventricle, which pumps it to the lungs to pick up oxygen.
- Oxygenated blood from the lungs enters the left atrium and flows into the left ventricle, which pumps it out to the body.
- Valves: The heart has valves that ensure blood flows in one direction. The main valves are:
- Tricuspid (between right atrium and ventricle)
- Pulmonary (between right ventricle and lungs)
- Mitral (between left atrium and ventricle)
- Aortic (between left ventricle and the aorta, the main artery carrying blood to the body)
- Major Blood Vessels: These vessels transport blood into and out of the heart:
- Vena Cavae (Superior and Inferior): Large veins that bring deoxygenated blood from the body into the right atrium.
- Pulmonary Artery: Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs.
- Pulmonary Veins: Carry oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
- Aorta: The body’s largest artery, carrying oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the rest of the body.
Weight of Heart
- The normal weight of a human heart varies, but typically ranges from approximately 220-350 grams for adults, with male hearts heavier than female
- Adult male hearts usually weigh about 280-340 grams, while adult female hearts are typically 230-280 grams.
This basic structure allows the heart to efficiently pump blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs.

