This is how the AI article summary could look. Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat.
10 Common Thyroid Problems – When to Worry and When to See a Doctor
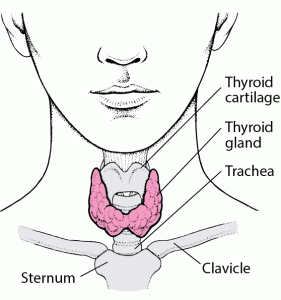
The thyroid gland is a vital endocrine organ that regulates metabolism, growth, and development. Thyroid disorders are common and can present in various ways, making diagnosis and management challenging.
Thyroid problems are dealt with by your GP, and a hospital physician (endocrinologist) and surgeon (endocrine). Here are 10 common thyroid problems, their symptoms, and when to worry and see a doctor.
1. Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
- Symptoms: Fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, slowed heart rate, depression, memory lapses, and muscle weakness.
- Causes: Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, thyroid surgery, or existing conditions like coeliac disease or lupus (SLE).
- When to Worry: Persistent symptoms, especially in patients with a history of thyroid surgery or radiation exposure.
- When to See a Doctor: If symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment, or if the patient has a history of thyroid disease.
2. Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
- Symptoms: Rapid heart rate, anxiety, weight loss, sleep troubles, excessive sweating, and muscle weakness.
- Causes: Graves’ disease, thyroid nodules, or thyroiditis.
- When to Worry: Severe symptoms, thyroid storm, or cardiac complications (e.g. atrial fibrillation, AF).
- When to See a Doctor: If symptoms are severe, or if the patient has a history of thyroid disease or cardiac conditions.
3. Goitre
- Symptoms: Enlargement of the thyroid gland, neck tightness, breathing difficulties, or coughing.
- Causes: Iodine deficiency, thyroid nodules, or thyroiditis.
- When to Worry: Rapid growth, tracheal compression, or suspected malignancy.
- When to See a Doctor: If the goitre is large, growing, or causing compressive symptoms.
4. Thyroid Nodule
- Symptoms: Lumps in or on the thyroid gland, potentially causing hyperthyroidism or goitre.
- Causes: Benign or malignant tumour, cyst, or inflammation.
- When to Worry: Suspicious ultrasound features, rapid growth, or compressive symptoms.
- When to See a Doctor: If the nodule is large (>1 cm), has suspicious features, or is causing symptoms.
5. Thyroid Cancer
- Symptoms: Thyroid nodule, neck lymphadenopathy, or vocal cord paralysis.
- Causes: Genetic mutations, radiation exposure, or family history.
- When to Worry: Suspicious nodule features, family history, or radiation exposure.
- When to See a Doctor: If a thyroid nodule is suspected to be malignant or has suspicious features.
6. Postpartum Thyroiditis
- Symptoms: Hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism, often within 6-12 months postpartum.
- Causes: Autoimmune response triggered by childbirth.
- When to Worry: Severe symptoms, thyroid storm, or persistent hypothyroidism.
- When to See a Doctor: If symptoms persist or worsen after childbirth, or if the patient has a history of thyroid disease.
7. Painless Thyroiditis
- Symptoms: Hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism, often without thyroid pain.
- Causes: Autoimmune response or viral infection.
- When to Worry: Severe symptoms, thyroid storm, or persistent hypothyroidism.
- When to See a Doctor: If symptoms persist or worsen, or if the patient has a history of thyroid disease.
8. Subacute Thyroiditis
- Symptoms: Painful thyroid gland, fever, muscle aches, and tiredness.
- Causes: Viral infection.
- When to Worry: Severe symptoms, thyroid storm, or abscess formation.
- When to See a Doctor: If symptoms are severe, or if the patient has a history of thyroid disease or cardiac conditions.
9. Riedel Thyroiditis
- Symptoms: Hard, fibrotic thyroid gland, potentially causing compressive symptoms.
- Causes: Unknown, possibly autoimmune.
- When to Worry: Compressive symptoms, suspected malignancy, or rapid progression.
- When to See a Doctor: If the patient presents with a hard, fixed thyroid gland or compressive symptoms.
10. Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis
- Symptoms: Hypothyroidism, goitre, or thyroid nodules.
- Causes: Autoimmune.
- When to Worry: Persistent or worsening hypothyroidism, or suspected malignancy.
- When to See a Doctor: If symptoms persist or worsen despite treatment, or if the patient has a history of thyroid disease.
Conclusion
Thyroid disorders are common and can present in various ways. It is essential to recognise these conditions and know when to worry and see a doctor. Early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve patient outcomes. Always refer to current guidelines and consult with senior colleagues when managing thyroid disorders.