What are the 5 most important hospital acquired infections (HAIs)? In this article we will describe what are the 5 most important hospital acquired infections (HAIs). First of all. How common are HAIs? Quite common. It is estimated that 5-10% of patients in an acute hospital have an HAI at any one time. The most common HAIs […]
Read MoreHow long do viral infections last for? In most people, most viral infections last 2-3 days. But, at worst, they can also last a lifetime (see below). In this article will describe how long most viral infections last for. What are viruses? Viruses are tiny germs that can only be seen under a microscope. They […]
Read More10 most common STDs In this article we will describe the 10 most common STDs, and their treatments. 1. Chlamydia Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted disease (STD). It is caused by a bacterium called Chlamydia trachomatis. Symptoms: Chlamydia is mostly asymptomatic with studies suggesting 10% of men and 5-30% women developing symptoms. Women: Pain when urinating […]
Read MoreHow to prevent STDs In this article we will describe 5 ways to prevent sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Let’s start with the basics. Vaccinations can prevent STDs (see below) What is a STD? Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are infections usually acquired though unprotected sexual contact with someone who’s infected. But, you cannot always tell if […]
Read More10 Essential Facts About Fever: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Fever is a common health concern, often signalling an underlying condition. Understanding what causes it, how it affects the body, and when to seek medical attention can help you manage it effectively. Here are 10 key facts about fever in adults. 1. What is a Fever? […]
Read MoreA normal full blood count (FBC) A full blood count has three main components: Haemoglobin (‘Hb’) 130-170 g/L for men 110-150 g/L for women White cell count (WC) = 4-11 x10^9/L (million per litre) Platelet count = 150-400 x10^9/L (million per litre). Here is more information on these three components. 1. Haemoglobin (‘Hb’) For adults, normal […]
Read MoreKidney blood tests – what’s normal and abnormal? Keep track of your kidney data with PKB Kidney doctors love blood tests. Full stop. Why? It is because it is impossible for them to judge the function of the kidneys solely by asking you questions (doctors call this the ‘history’) and physical examination. So, what is […]
Read MoreHow is CKD defined? Keep track of your kidney data with PKB It is surprisingly difficult to answer. This is partly because chronic kidney disease (CKD) is not a diagnosis. It is a syndrome (group of diseases) with many specific causes (diagnoses). Nonetheless .. here goes. Key points Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is defined as […]
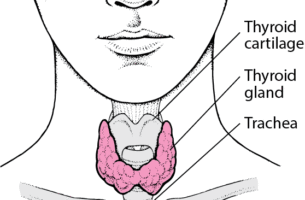
Read MoreMild underactive thyroid (hypothyroidism): who should be treated? Normal thyroid blood tests TSH: 0.5 – 5.0 mU/L. This is the most important test Free thyroxine (T4): 8.0 – 18.0 pmol/L. How is an underactive thyroid gland diagnosed? A high TSH and low thyroxine (T4) indicates an underactive thyroid gland (hypothyroidism) – and requires treatment with thyroxine […]
Read MoreWhat is normal saline – and how is it used? Normal saline, also known as isotonic saline or 0.9% saline, is a solution of salt (sodium chloride, NaCl) in water. It has a concentration of 9 grams of sodium chloride per litre of water, which is roughly equivalent to the concentration of sodium chloride in […]
Read More